What is one benefit of the CAM system?
When it comes to Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems, it's easy to get caught up in the multitude of features and capabilities they offer....
3 min read
![]() Toolpath
:
Updated on February 10, 2025
Toolpath
:
Updated on February 10, 2025
If you’re working adjacent to CNC machining, you’ve probably heard the terms CAD, CAM, and automation tossed around. While these tools are often mentioned together, each one plays a distinct role in modern manufacturing. Understanding the difference between CAD (Computer-Aided Design), CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), and automation is foundational in starting to understand how to maximize efficiency and precision in your shop. Let’s break it down.
CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, is about planning and creating a product. Think of CAD as the digital sketchpad where your ideas come to life. Engineers and designers use CAD software to create detailed models and drawings, which can include:
Dimensions
Material specifications
Tolerances
These designs are often 3D models that provide a visual and technical blueprint for the final product.
Precision design: CAD software ensures that every detail is accounted for.
Easy modifications: Adjust designs quickly without starting from scratch.
Collaboration: Share files easily with team members and clients.
CAM, or Computer-Aided Manufacturing, picks up where CAD leaves off. CAM software translates CAD models into machine-readable instructions (like G-code) that your CNC machines can execute. In simpler terms, CAM is how you turn your design into a physical product.
Import CAD files: 2D and 3D CAD geometry is imported into CAM software, where it is used to create paths for the CNC machine to follow.
Generate toolpaths: With automated toolpath creation, the software calculates the most efficient way for the machine to cut, drill, or mill the material.
Program CNC machines: The instructions (G-code) are sent to the CNC machine, which carries out the work.
Seamless CAD integration:
Support for all the major CAD file formats
Toolpath generation and editing:
Broad range of toolpath types to support various geometry types. The passes should be efficient and generated quickly.
Simulation and CNC post-processing:
Built-in simulation catches errors early while post-processing fine-tunes CNC code for smooth, error-free production.
For more insights into leveraging CAM effectively, check out Mastering CAM Automation: A Guide For CNC Shops.
Automation ties CAD and CAM together, streamlining the entire process from design to production by reducing manual intervention.
Automation is essential for modern shops, especially when aiming for efficient CNC machining processes or implementing smart CAM strategies for machinists.
Think of these three as parts of a unified system:
| Feature | CAD | CAM | Automation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Design creation | Manufacturing programming | Workflow efficiency |
| Focus | Product design | Turning design into instructions | Streamlining the entire process |
| Key Benefit | Precision | Efficiency | Reduced human intervention |
| Technology Integration | Works with CAM | Works with CAD and CNC machines | Links all systems seamlessly |
While CAD, CAM, and automation are powerful individually, they shine together. CAD gives you precise and modifiable designs, CAM transforms those designs into practical production plans, and automation ensures that the entire process runs smoothly and efficiently. This integrated approach minimizes errors and maximizes productivity.
CAD ensures that your designs are accurate and detailed.
CAM turns those designs into actionable instructions for your machines.
Automation ties it all together, creating a streamlined workflow that minimizes errors and maximizes productivity.
Of the three, CAM often feels like the workhorse. It’s where your designs come to life through automation and intelligent programming. Features like CAM automation for small shops make it accessible for operations of all sizes. Here’s why CAM is critical:
Time savings: Automating toolpaths and programming means faster setups.
Cost efficiency: Optimized processes reduce material waste.
Scalability: CAM grows with your shop, whether running one machine or twenty.
To get the most out of your CAM software, adopt these smart CAM strategies:
Automate repetitive tasks: Free up machinists for more complex jobs.
Leverage AI tools: Use AI-driven insights to improve machining efficiency.
Integrate systems: Seamlessly connect your CAD, CAM, and CNC systems.
Toolpath simplifies the integration of CAD, CAM, and automation with:
Cloud-based CAM solutions: Access your projects anywhere.
Automated toolpath creation: Save time and improve accuracy.
Intelligent CNC programming: AI-driven tools for smarter machining.
The difference between CAD, CAM, and automation lies in their roles, but their combined impact is where the magic happens. Together, they enable precision design, efficient manufacturing, and streamlined workflows. Investing in tools like Toolpath’s CAM software ensures you’re set up for success in every process step.
Ready to elevate your shop’s capabilities? Start Your Free Trial Today and experience the difference CAD, CAM, and automation can make.

When it comes to Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems, it's easy to get caught up in the multitude of features and capabilities they offer....
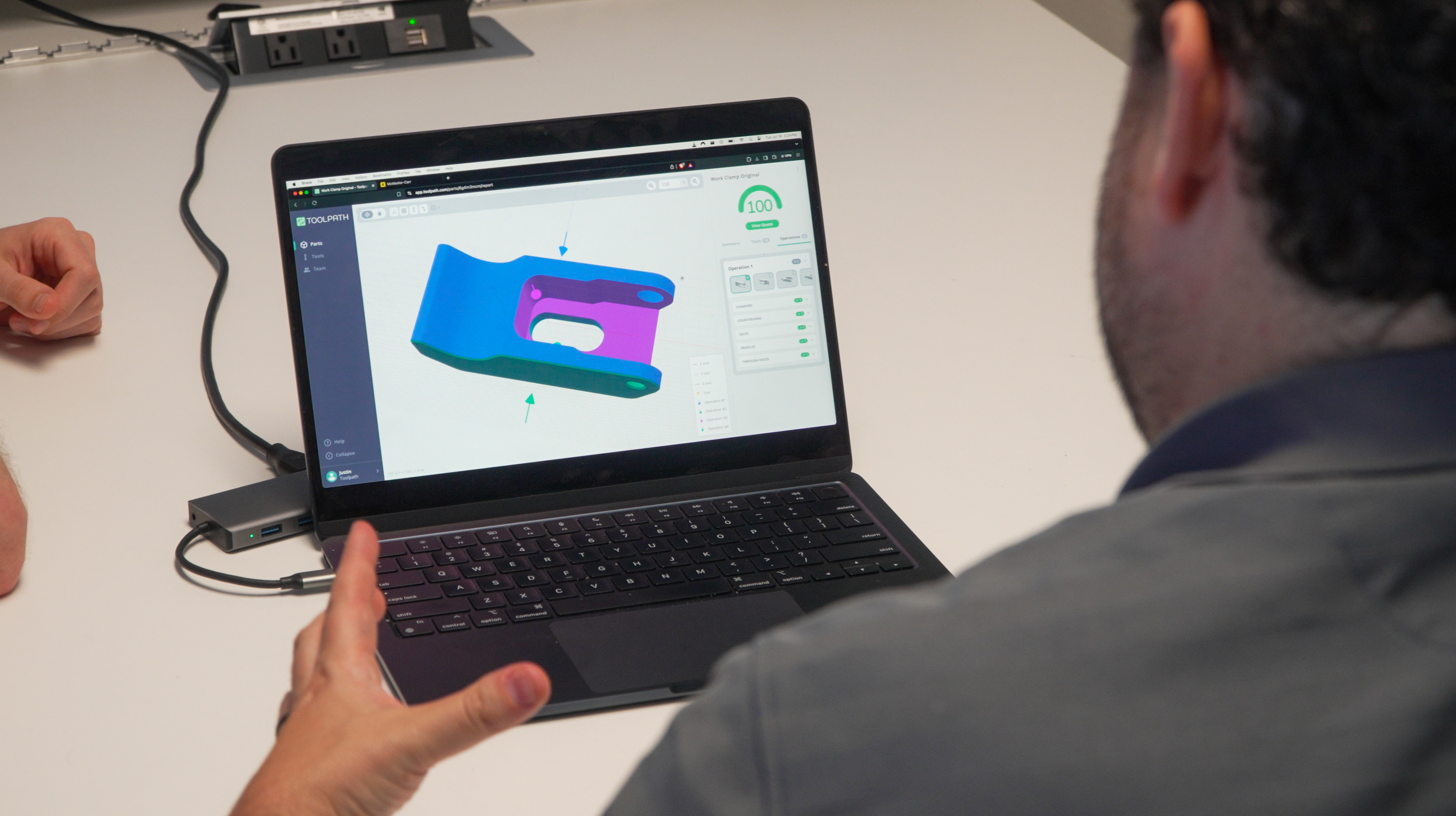

In the fast-paced world of modern manufacturing, Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software has become an indispensable tool for enhancing...
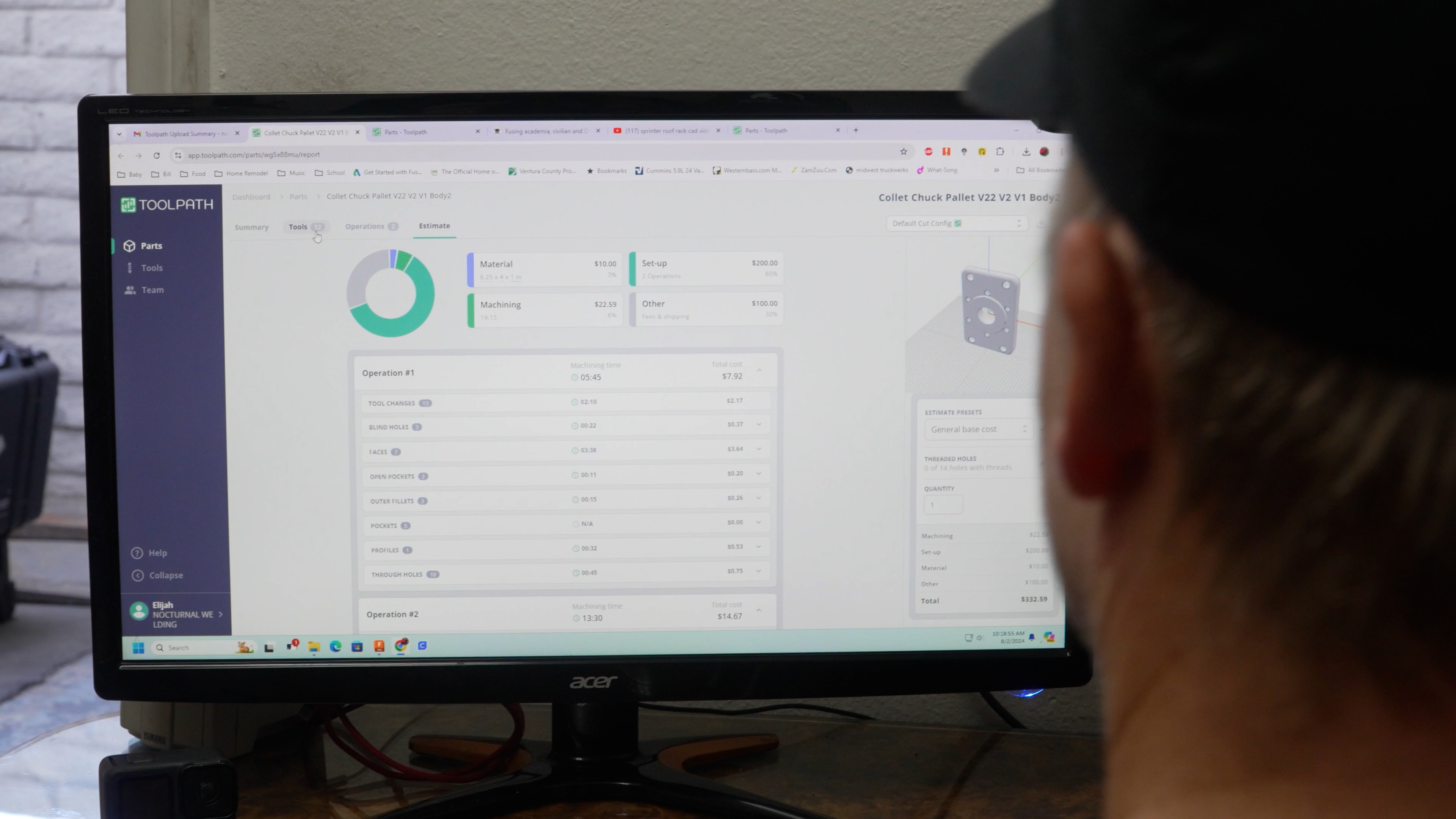
Are you new to CNC machining and wondering about CAM software? Think of CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) as your skilled interpreter, translating...

Picture this: You're a machinist tasked with creating a complex part, one with intricate curves, tight tolerances, and a deadline that's fast...

Choosing the right CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software isn’t just about picking a tool; it’s about finding a solution that fits your...

In today's rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, choosing the right Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software can make or break your CNC shop's...