What is the most widely used CAM software?
In the fast-paced world of modern manufacturing, Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software has become an indispensable tool for enhancing...
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology has become the backbone of modern manufacturing automation. CNC machines have revolutionized the way products are made by combining the precision and repeatability of computer control with the versatility of various machining processes. In this post, we'll explore how CNC is used in automation and the tools and strategies that enable CNC machines to operate with unparalleled efficiency.
At its core, CNC automation involves using computer software and controls to operate machine tools. Instead of relying on manual operation, CNC machines execute pre-programmed sequences of instructions, allowing them to perform complex machining tasks with minimal human intervention.
To understand how CNC enables automation, let's break it down into a few key components:
Combining these elements allows CNC machines to execute complex machining processes with minimal human intervention, making them a key enabler of automation in modern manufacturing.
While CNC machines provide the physical means of automation, it's the software that truly unlocks their potential. Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software plays a crucial role in CNC automation by simplifying the process of creating machine-ready programs.
Here's how CAM software streamlines the programming process:
By automating these critical programming tasks, CAM software significantly reduces programming time and effort, allowing manufacturers to get parts to production faster.
While the right hardware and software are essential for CNC automation, it's equally important to implement smart strategies that maximize efficiency and productivity. Here are a few key strategies to consider:
By combining these strategies with the power of CNC automation, manufacturers can achieve significant gains in productivity, quality, and profitability.
To better understand the impact of CNC automation, let's look at a few real-world examples:
These examples showcase the versatility and power of CNC automation in driving manufacturing efficiency across diverse industries.
CNC technology is at the heart of modern manufacturing automation, enabling the production of complex, high-precision parts with unprecedented efficiency. CNC machines have transformed the way products are made by leveraging the power of computer control, numerical precision, and programmability.
However, achieving the full benefits of CNC automation requires more than just the right hardware. It involves the strategic use of CAM software, the implementation of smart machining strategies, and a mindset of continuous improvement.
If you're looking to improve your CNC operations, Toolpath's comprehensive guide, "Mastering CAM Automation: A Guide for CNC Shops," is a great resource. This in-depth guide covers everything from the fundamentals of CNC automation to advanced strategies for optimizing your machining processes.
Ready to experience the power of CNC automation firsthand? Start your free trial of Toolpath's cutting-edge CAM software today and discover how our AI-driven tools and intuitive interface can help you unlock new levels of efficiency and productivity in your CNC operations.
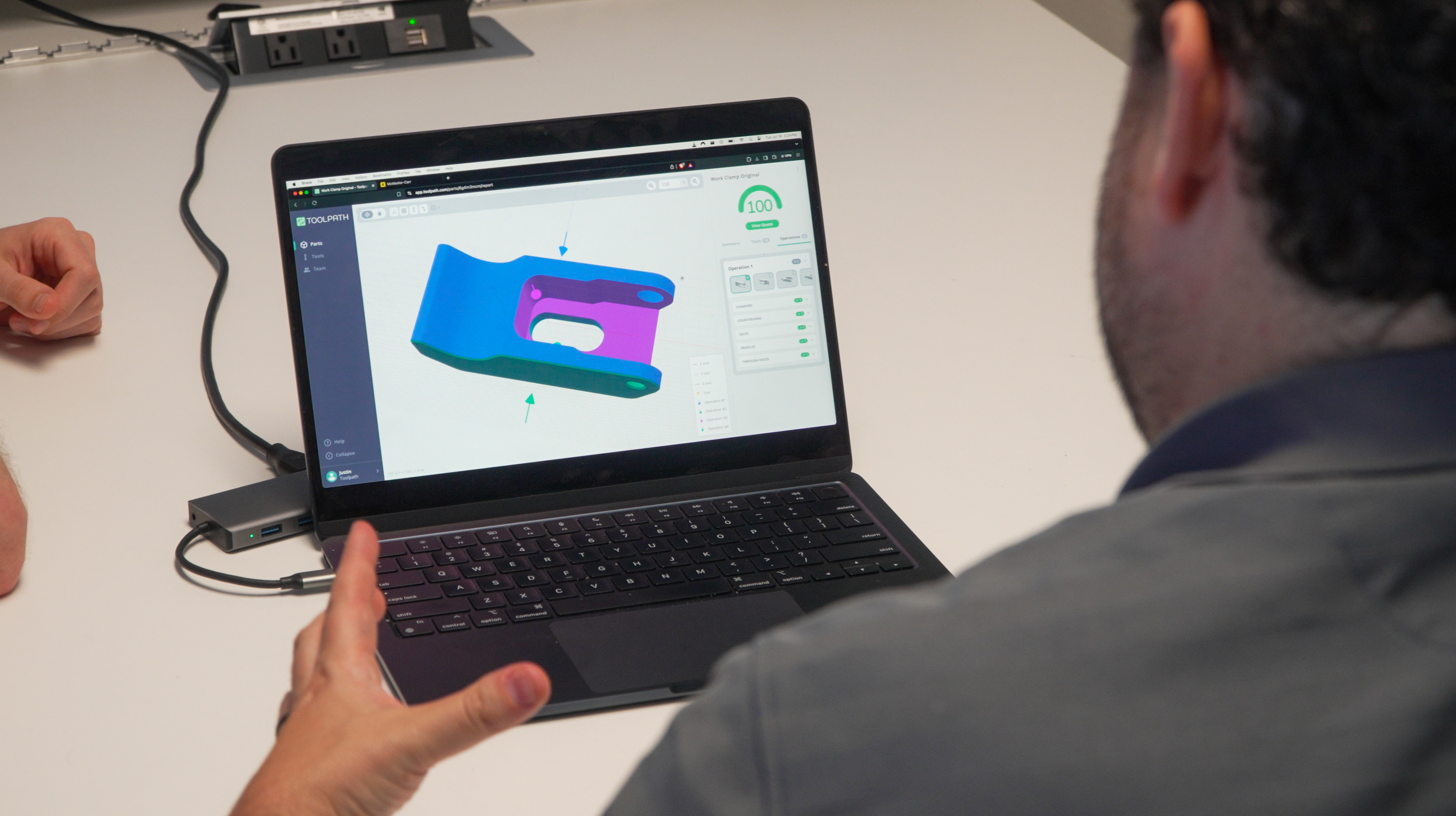

In the fast-paced world of modern manufacturing, Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software has become an indispensable tool for enhancing...

Picture this: You're a machinist tasked with creating a complex part, one with intricate curves, tight tolerances, and a deadline that's fast...
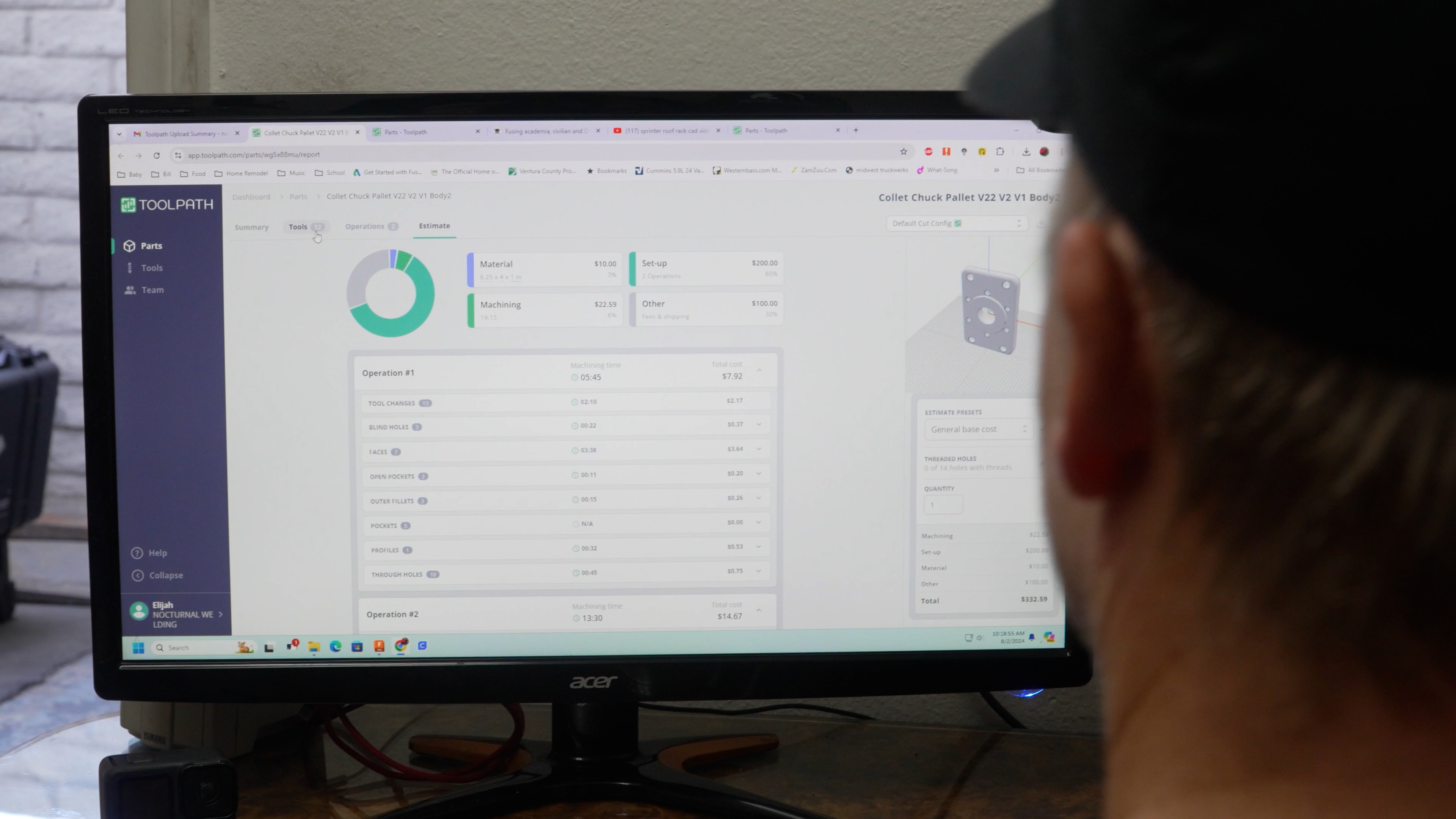
Are you new to CNC machining and wondering about CAM software? Think of CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) as your skilled interpreter, translating...
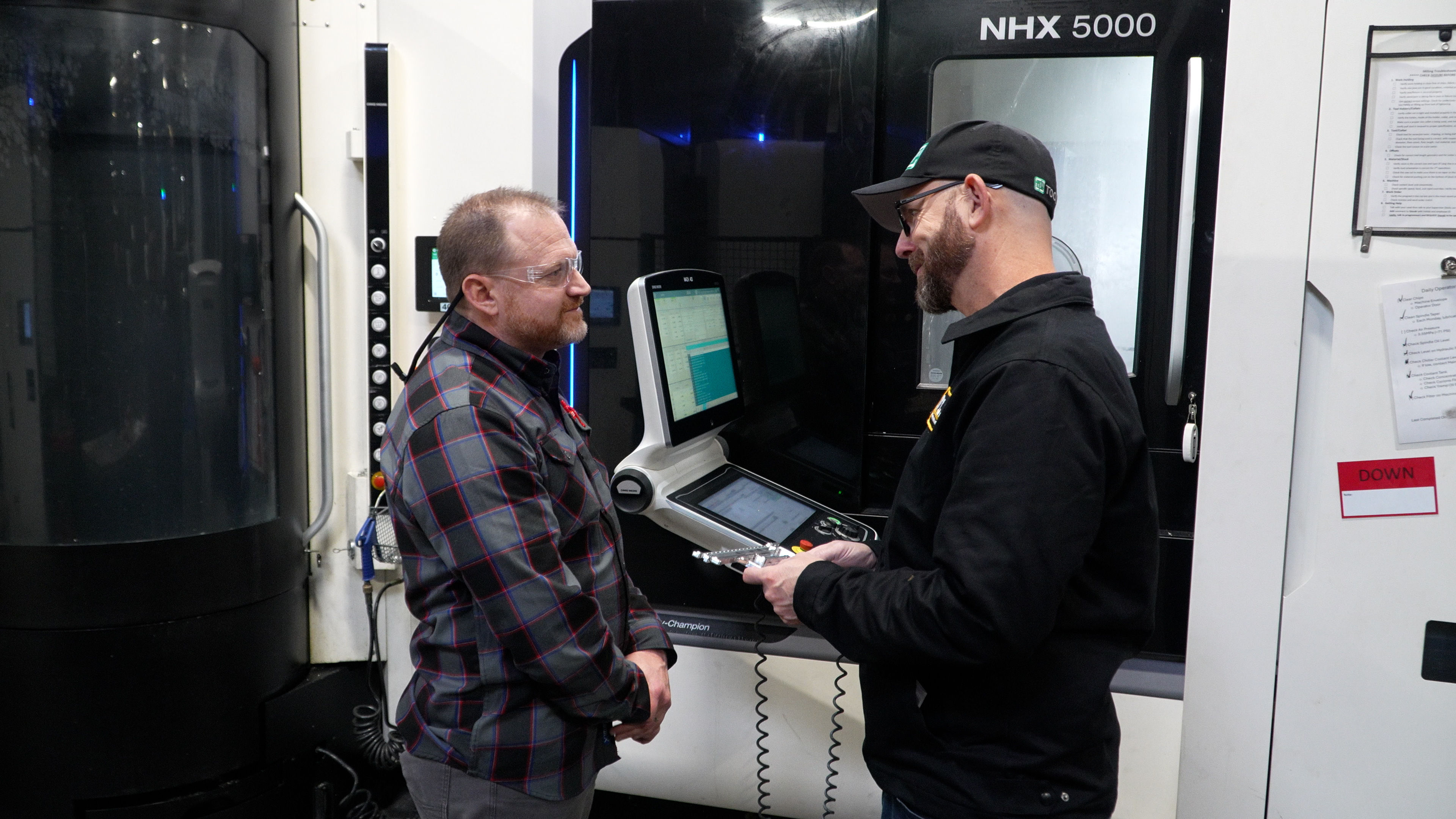

When it comes to Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems, it's easy to get caught up in the multitude of features and capabilities they offer....
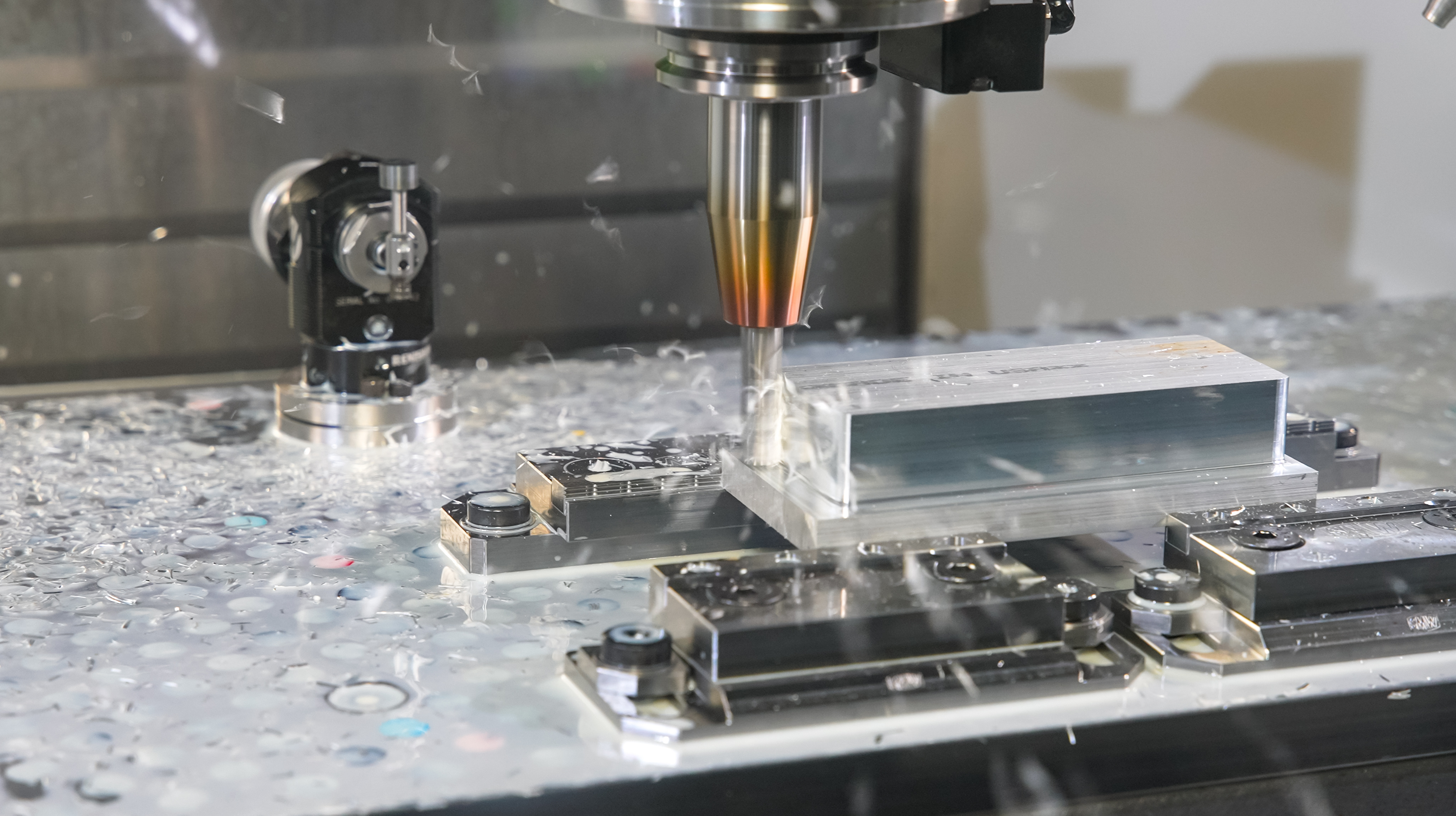

Choosing the right CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software isn’t just about picking a tool; it’s about finding a solution that fits your...
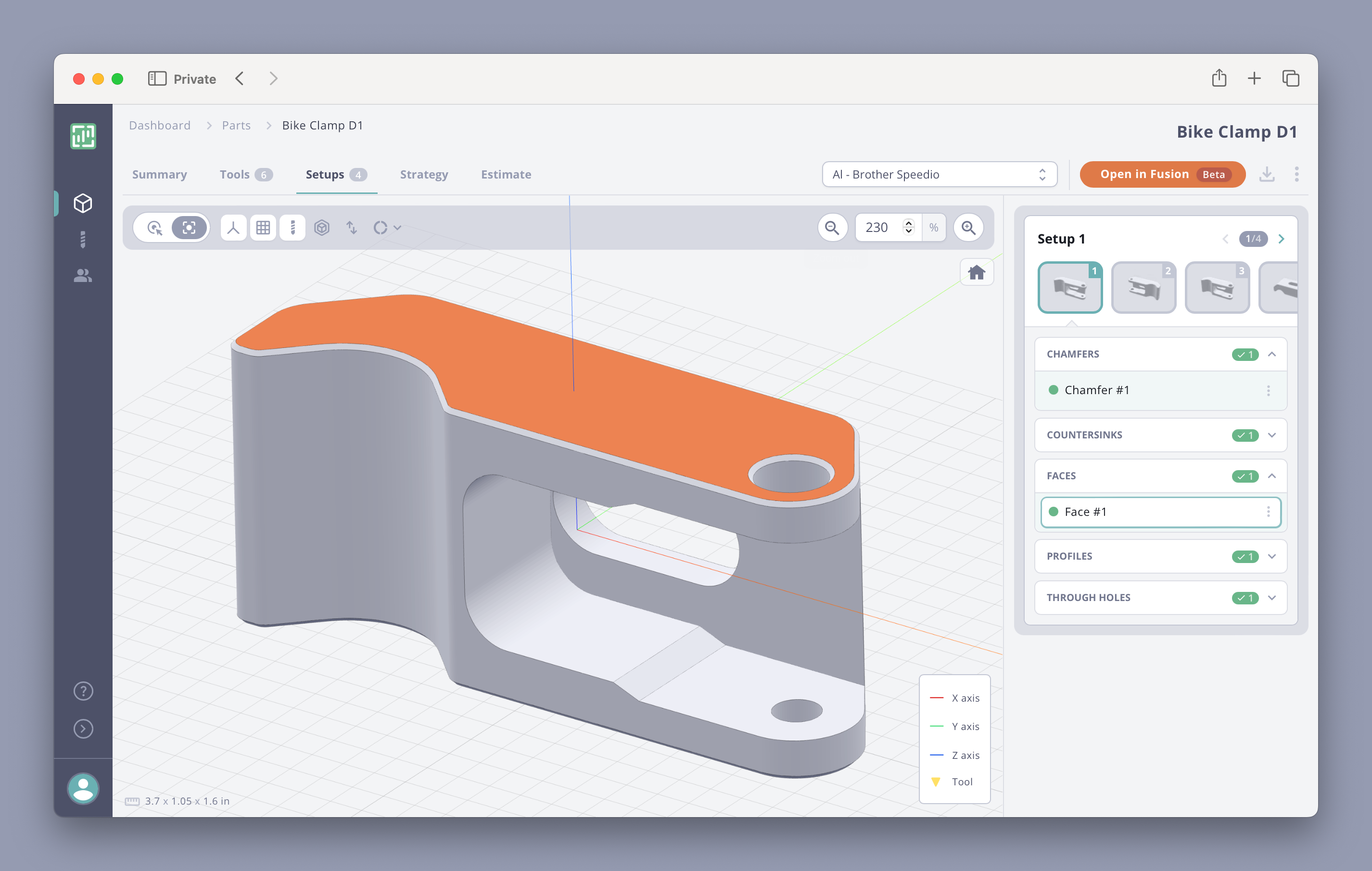
If you’re working adjacent to CNC machining, you’ve probably heard the terms CAD, CAM, and automation tossed around. While these tools are often...